A presentation by the City of Wichita regarding IRBs is good as far as it goes, which is not far enough.
Recently the City of Wichita prepared a short video explaining the city’s industrial revenue bonds (IRB) program. The video may be viewed on YouTube by clicking here.
Several times the presenters emphasized that in the IRB program, the city does not lend money. They properly identify the true purpose of the program, which is to subsidize companies by allowing them to avoid paying property taxes and possibly sales taxes.
Several times the presenters emphasized that the IRB program has no cost to the city. But that isn’t true. Part of the rationale for taxes, especially the property taxes that cities, counties, and school districts collect, is to pay for services that people and business firms demand. Well, don’t new businesses firms demand or require services from the government? And if a business is not paying its share of taxes, who is paying for the services it consumes?
If we don’t think that a new or expanded business spurs demand for services, then we need to rethink the basis of taxation.
The presenters mentioned the benefit-cost analysis produced for the city by Center for Economic Development and Business Research at Wichita State University and concluded that the city profits from the IRB program. This analysis purports that if the city incurs costs — either by spending one dollar or giving up one dollar of tax revenue — it will receive a certain amount in return. City policy requires that the city receive $1.30 or more in benefits for each dollar of cost. But there are issues:
- The city says IRBs have no cost, but the benefit-cost ratio identifies costs. The city hopes the benefits outweigh these costs.
- There is no guarantee that the city will receive any benefits, or that the benefits will be close to what the CEDBR model estimates.
- The CEDBR model asks companies to make projections of economic activity for up to ten years in the future. Especially in the out-years, these estimates are subject to large errors.
- No effort is made to scrutinize these projections. They are taken at face value, as supplied by the applicant company.
- The benefits to the city are in the form of taxes paid. Taxes are a burden to those who must pay them.
- Applicant companies do not have to demonstrate economic necessity.
- The policy of requiring a benefit of $1.30 for each dollar of cost has many loopholes.
Perhaps the most important policy issue is that the city realizes the benefits of increased economic activity whether or not the activity is subsidized with IRB tax breaks. The benefit-cost ratio for unsubsidized projects is infinite: All benefit, no cost. Therefore, the benefit-cost ratio is meaningful only for those projects which could not proceed without the subsidy.
Some incentive programs require the demonstration of economic necessity. That is not the case with IRBs.
Additionally, when the city issues IRBs and grants tax abatements, other jurisdictions are affected. Both the overlapping county and school district have their property tax collections eliminated. If a sales tax exemption is granted, the state is most prominently affected, as nearly all sales tax paid goes to the state. (For sales tax paid in Sedgwick county, the state’s share is 86.7 percent.) None of these overlapping jurisdictions can opt-out of the tax abatement that the city imposes.



 Even over the ten-year life of the property tax abatement, the sales tax exemption is still 11.8 percent of the total tax forgiveness. That — the duration of the property tax abatement — is another opportunity to increase transparency. The CEDBR analysis gives the total cost of the incentives for ten years. (A nearby table summarizes.) These totals are speculative, as the city council must revisit the matter in five years to determine whether the company deserves the property tax abatement for an additional five years. (This is known as a “five-plus-five year tax exemption.”)
Even over the ten-year life of the property tax abatement, the sales tax exemption is still 11.8 percent of the total tax forgiveness. That — the duration of the property tax abatement — is another opportunity to increase transparency. The CEDBR analysis gives the total cost of the incentives for ten years. (A nearby table summarizes.) These totals are speculative, as the city council must revisit the matter in five years to determine whether the company deserves the property tax abatement for an additional five years. (This is known as a “five-plus-five year tax exemption.”)


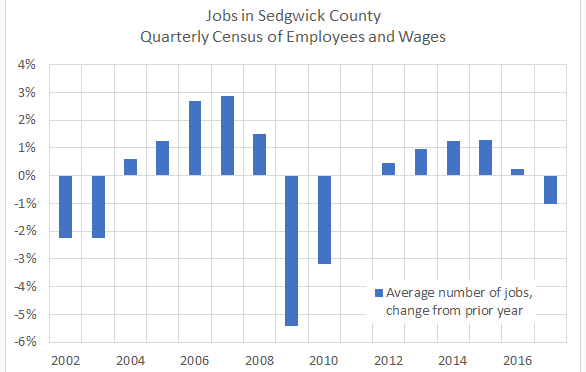




 Many will undoubtedly cheer the Spirit announcement as an economic development win on a large scale. It will add many jobs. But the Wichita-area economy is so far behind it will take much more growth than this to catch up with the rest of the nation. In fact, the Wichita-area economy shrank last year.
Many will undoubtedly cheer the Spirit announcement as an economic development win on a large scale. It will add many jobs. But the Wichita-area economy is so far behind it will take much more growth than this to catch up with the rest of the nation. In fact, the Wichita-area economy shrank last year. 