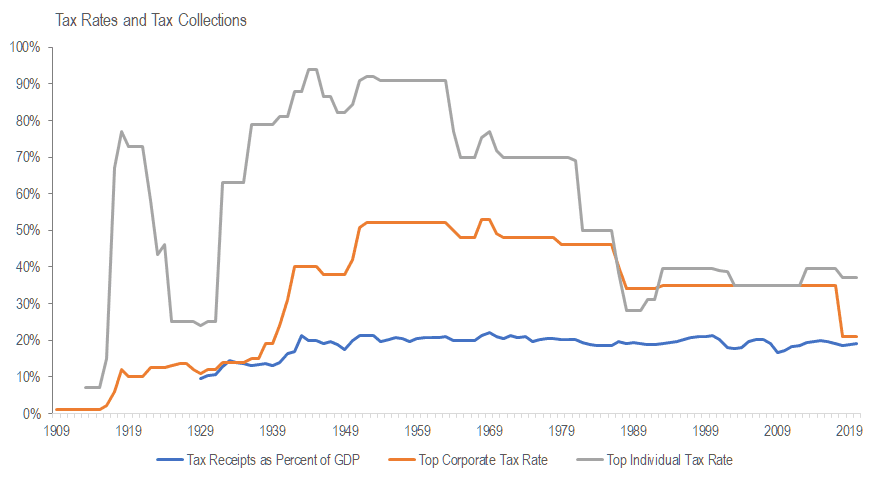
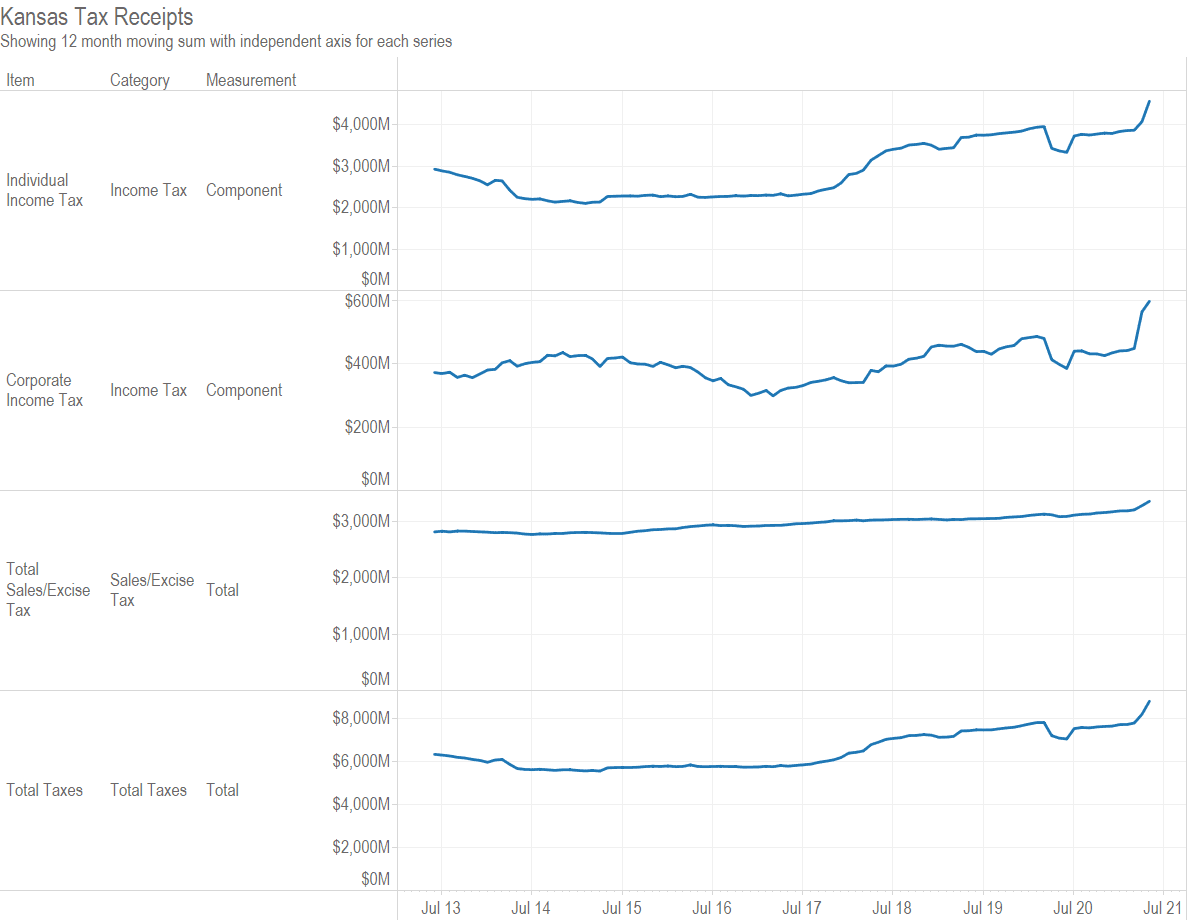
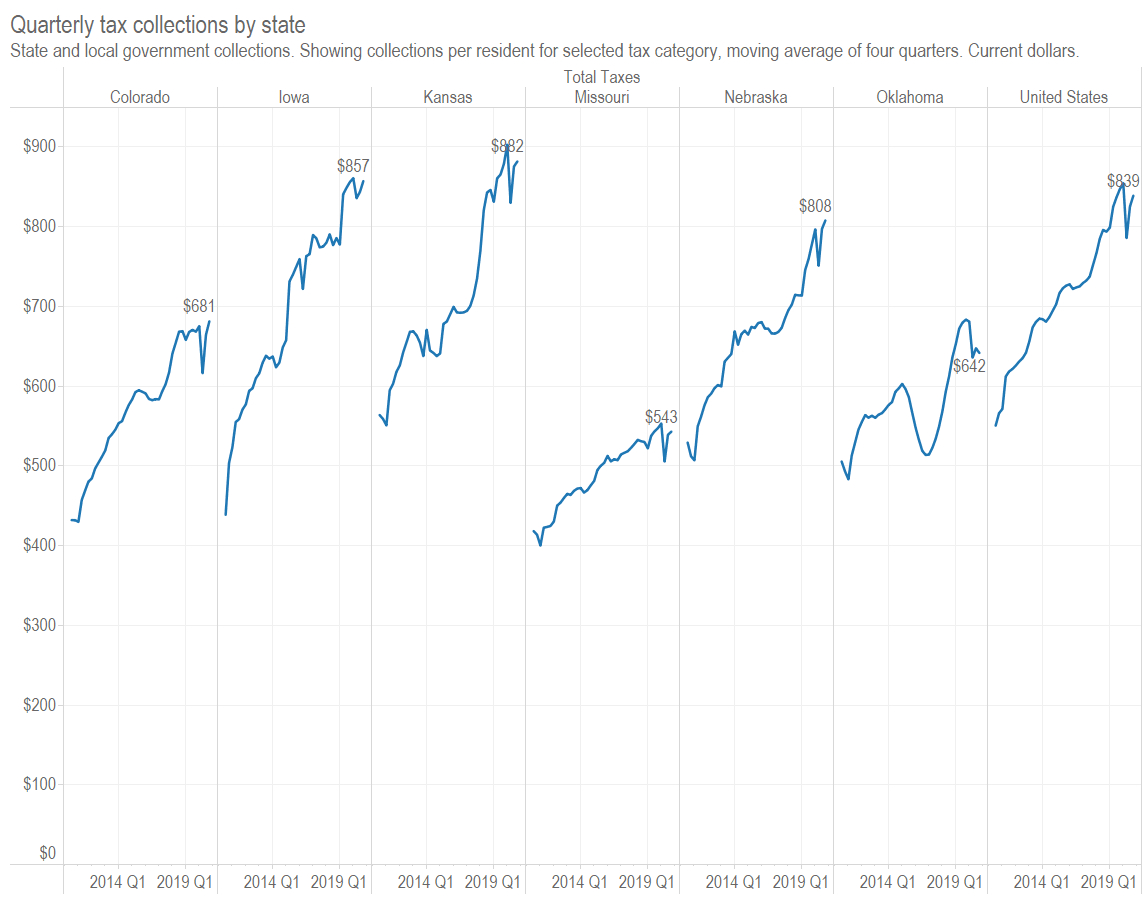
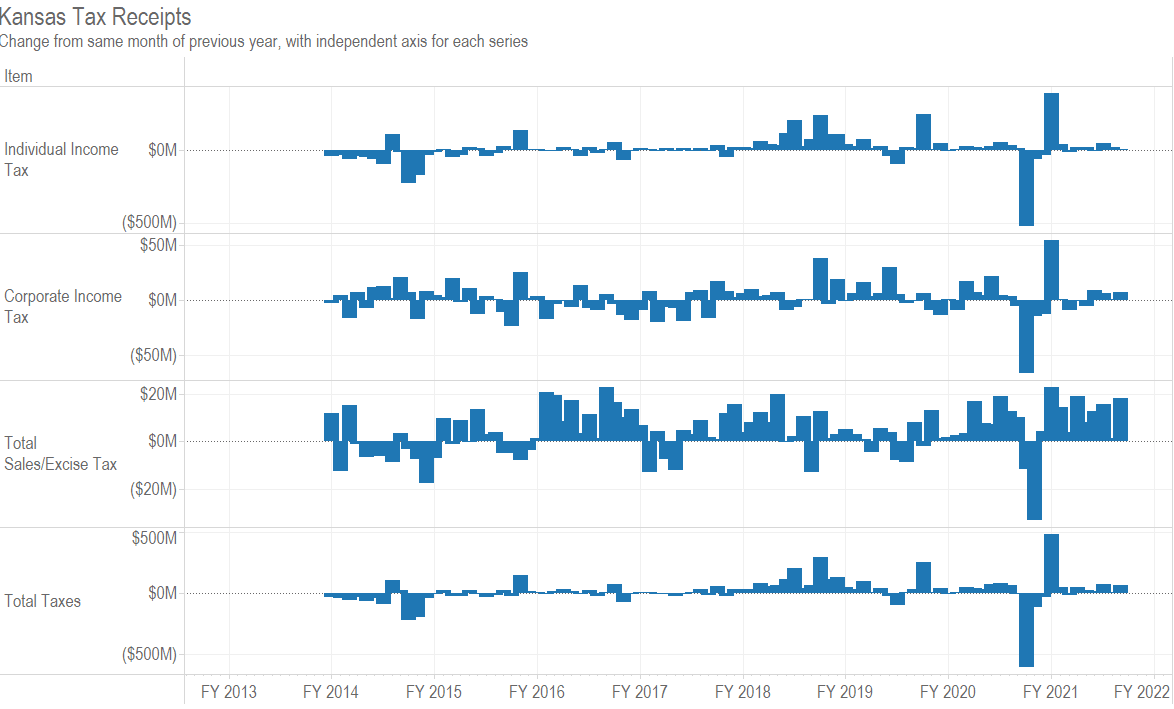
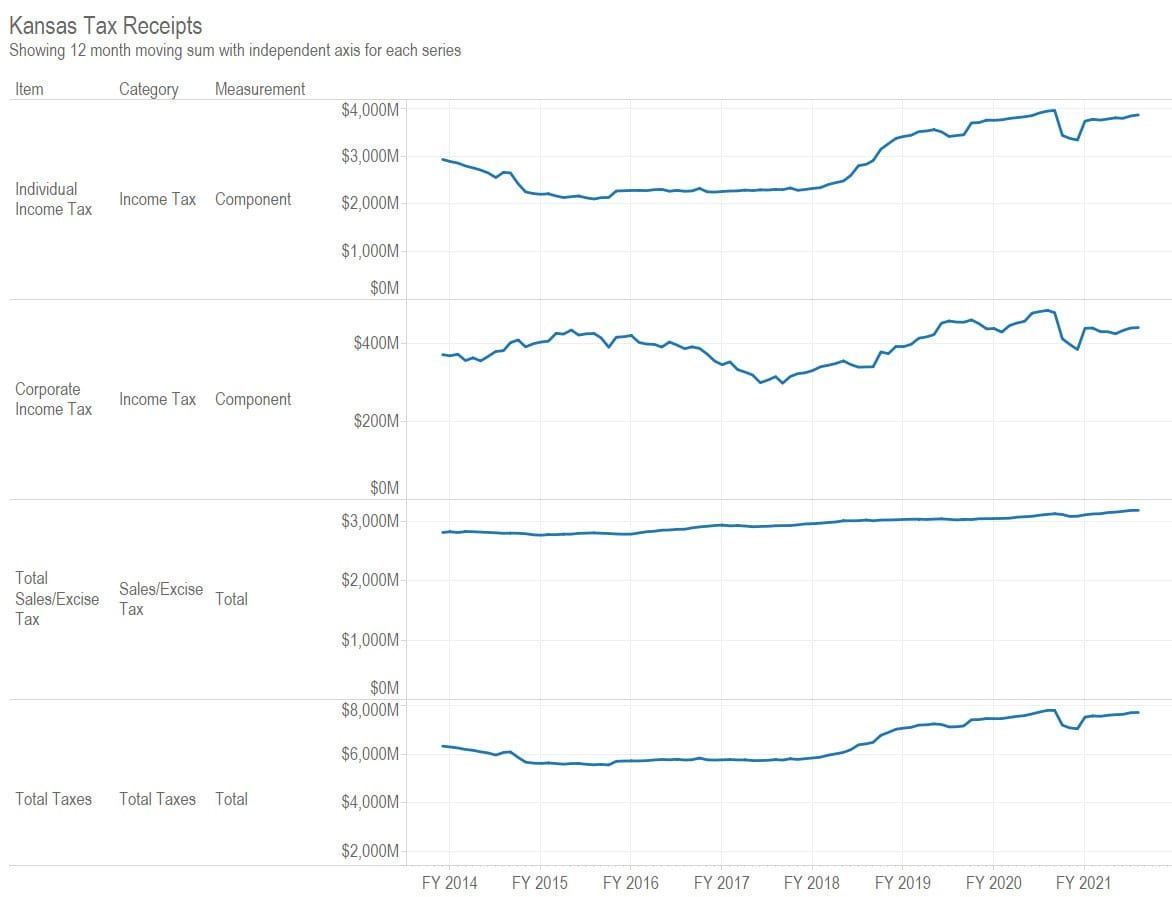
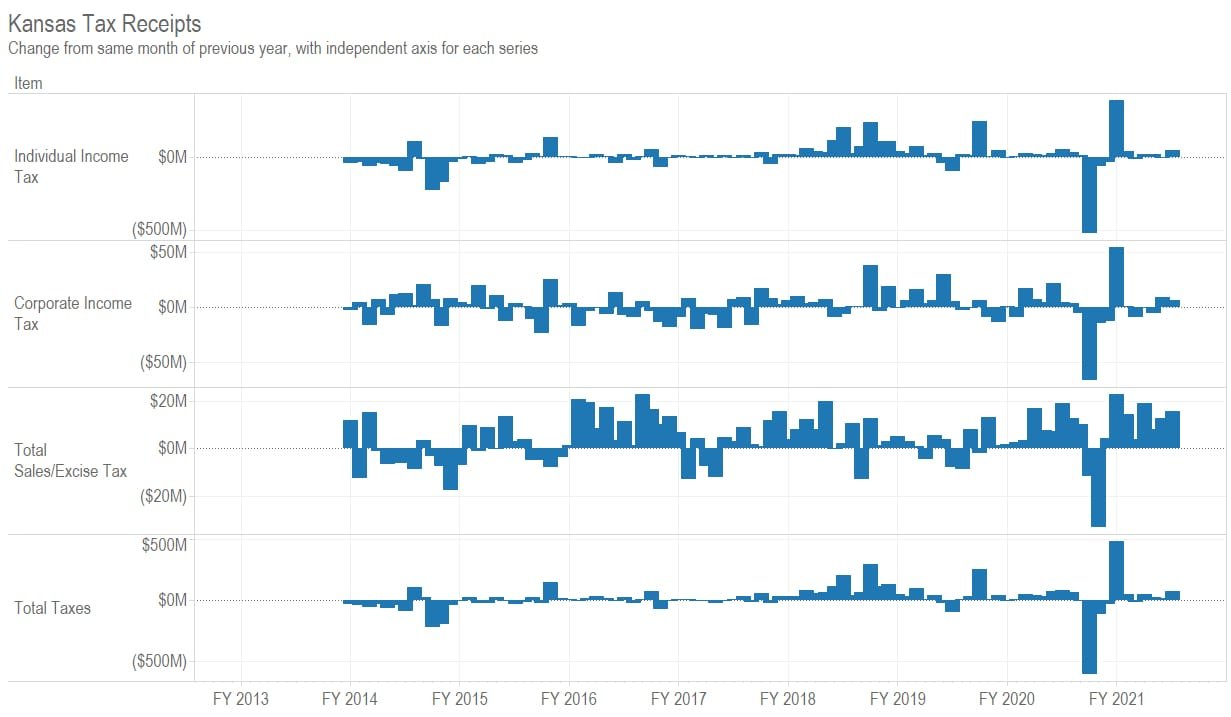
Is there a relationship between marginal tax rates and tax dollars collected? Not much. (more…)
Tag: Taxation

Kansas tax revenue, May 2021
For May 2021, Kansas tax revenue was 134.7 percent greater than May 2020. Over the eleven months of the current fiscal year, revenue is 27.7 percent higher than at the same point of the previous year. There are important caveats to consider. (more…)

Kansas tax revenue, April 2021
For April 2021, Kansas tax revenue was 69.9 percent greater than April 2020. Over the ten months of the current fiscal year, revenue is 19.5 percent higher than at the same point of the previous year. There are caveats to consider. (more…)

Quarterly tax collections
Tax collections by state and local governments fell by about one percent during calendar year 2020 when compared to the year before.
Tax collection data from the United States Census Bureau shows state and local government tax collections falling only slightly during 2020, despite the effects of the pandemic. (more…)

Kansas tax revenue, March 2021
For March 2021, Kansas tax revenue was 12.7 percent greater than March 2020. Over the nine months of the current fiscal year, revenue is 14.0 percent higher than at the same point of the previous year. (more…)

Kansas tax revenue, February 2021
For February 2021, Kansas tax revenue was 1.7 percent greater than February 2020. Over the eight months of the current fiscal year, revenue is 14.2 percent higher than at the same point of the previous year.
Tax reports from the State of Kansas for February 2021 show tax revenues falling from the previous month, but higher than the same month the prior year, despite the effects of the response to the pandemic. The fall from January is characteristic of the seasonal pattern.
When reporting on Kansas tax collections, the comparison is usually made to the estimated collections. Those estimates were revised in April 2020 based on economic conditions affected by the response to the pandemic. To get a feel for the effects of the response to the pandemic, it is best to compare to the same month the prior year.
(The estimated revenue figures are still important because the state budget is based on them. If the actual revenue is much below the estimated revenue, there may not be enough income to pay expenses.)
For February 2021, individual income tax collections were $193.7 million, up by 13.0 percent from the prior February. Retail sales tax collections rose by 0.8 percent to $179.3 million. Total tax collections were $455.9 million, up 1.7 percent from the same month the prior year. A nearby table summarizes.

For fiscal year 2021, which started on July 1, 2020, total tax collections are up by 14.2 percent over the same period of the previous fiscal year. A large reason for this is the change in tax deadlines from April to July, shifting much revenue from fiscal year 2020 to fiscal year 2021. That hasn’t always been explained, as I show in In Kansas, explanations for tax collections may vary.
As can be seen in a nearby table, tax revenue for fiscal year 2021 is $673.9 million greater than at the same time in the previous fiscal year. Of this, $527.0 million, or 78.2 percent, is due to the increase in individual income tax revenue.

My report on tax revenue for April details some changes made by the estimating group.
My interactive visualization of Kansas tax revenue has been updated with October data. Click here to use it.
An example from the visualization illustrates the composition of Kansas tax revenue for the last year ending in November 2020. Individual income tax accounted for 50.5 percent of revenue, and retail sales tax 31.5 percent. Together, this is 82.0 percent. Add compensating use tax of 7.0 percent and corporate income tax of 5.6 percent, and that is nearly all — 94.6 percent — of Kansas tax revenue.
The governor’s press release for this data is at February Total Tax Collections Outperform Estimate by $19.8 million.

Say no to special tax treatment, again
In Kansas, a company seeks to avoid paying property taxes, again.
In a bill presented in the Kansas Legislature, the owner of health clubs seeks to avoid paying property taxes. The same company and its owner have tried this before. In 2014, I explained how granting this exemption was a bad idea.
What has changed since then? This exemption is still a bad idea for reasons of public policy. Additionally, Brandon Steven, the owner of the health clubs, plead guilty to a gambling charge and forfeited one million dollars in earnings. The companies also owe a lot of the tax it seeks to avoid.
Following, my article from March 2014.
Special interests struggle to keep special tax treatment
When a legislature is willing to grant special tax treatment, it sets up a battle to keep — or obtain — that status. Once a special class acquires preferential treatment, others will seek it too.
When preferential tax treatment is granted, that is, when government says someone doesn’t have to pay taxes, it’s usually the case that someone else has to pay. That’s because governmental bodies usually don’t reduce their spending in response to the tax breaks they give. Spending stays the same (or rises), but someone isn’t paying their share. Therefore, others have to make up the missing tax revenue.
In Kansas, SB 72 has been passed by the Senate and may be considered by the House of Representatives. This bill would, according to its supplemental note “provide a property or ad valorem tax exemption on all property owned and operated by a health club.” In effect, this bill would give all health clubs the same property tax exemption that the YMCA enjoys on its fitness centers.
When the legislature uses tax law to achieve goals, the statute book becomes complicated as illustrated by the many special sales tax exemptions in Kansas. K.S.A. 79-3606 details the special sales tax exemptions that the legislature has granted. In order to list them all, the statute has sections labeled from (a) through (z), then from (aa) through (zz), then from (aaa) through (zzz), and finally from (aaaa) through (gggg).
Some of these sections are needed and valuable, such as the section that exempts manufacturers from paying sales tax on component parts and ingredients used to build final products. It is supposed to be a retail sales tax, after all.
But then there are sections like this: “(vv) (18) the Ottawa Suzuki Strings, Inc., for the purpose of providing students and families with education and resources necessary to enable each child to develop fine character and musical ability to the fullest potential.”
I have no doubt that this organization is engaged in useful work and that there should be more of this. But what about all the other organizations engaged in similar activities, and which are undoubtedly as deserving of the same tax break? Should they be penalized because they did not have the temerity to ask?
In the area of property taxation, we find many similar circumstances, where two businesses that seem to be similarly situated are treated very differently by the tax collector.
For example, Wesley Medical Center, one of Wichita’s principal hospitals, is Wichita’s second-largest property taxpayer, with taxable assessed value representing 0.90 percent of the total of such property in Wichita.

One hospital has many millions in property, but is not taxed on that property. But another large Wichita Hospital, Via Christi Hospital on St. Francis, has assets valued at over $115 million, yet pays no property tax. For the mill levy rate that applies to its address, this represents about $3.5 million in property tax savings. (It did pay a Sedgwick County Solid Waste User Fee of $8.91.)
How can we meaningfully distinguish between Wesley and St. Francis Hospitals? Does one provide more charity care than the other? Does the non-profit hospital charge lower rates? (I’d be surprised if so.) Does St. Francis impose less of a burden on city and county resources such as fire and police protection than does Wesley? Since Wesley attempts to earn a profit and St. Francis purportedly does not, does that make Wesley evil and St. Francis saintly? Why do we exempt St. Francis from millions of property tax, yet insist it pay $8.91 in solid waste user fees?

A scene from a non-profit retirement living center. We find other examples: A luxury retirement community (Larksfield Place) with real property valued at $27,491,440 pays no property tax, except for $5.95 in the solid waste user fee. Less than a mile away, Sedgwick Plaza, a senior living center, has a valuation of $5,067,350 for its real property, and was billed $70,080.51 in property tax, including its solid waste user fee of $972. Despite — or perhaps due to — its non-profit status, Larksfield Place is able to provide its president a salary of over $130,000.
A Goodwill thrift store on West Central in Wichita has real property valued at $696,600, but paid no property taxes except for $5.94 solid waste user fee. On the other side of town, a small thrift store on East Douglas has real property valued at $113,800. It pays $3,437 in property tax, including its solid waste user fee.
These differences in what seem to be properties in similar situations are not justifiable under any theory of taxation, one of which is that similar situations are taxed similarly. The YMCA’s fitness centers are difficult to distinguish from others in Wichita — except for the YMCA’s rarefied tax-exempt status.
The slippery slope
Here’s the danger: Should SB 72 pass and all health clubs start enjoying the same tax privileges as the YMCA, shouldn’t we then expect to see for-profit hospitals like Wesley Medical Center ask to be relieved of their tax burden, using the same logic? If the legislature were to deny that request, how could it possibly explain its reasoning to citizens?
In defense of its tax exempt status, the YMCA says it engages in many charitable activities. I’m sure that’s true, and we’d like to keep those activities. Perhaps the YMCA would consider separating its fitness centers from the rest of its operations. Separate the business-like activities from the charitable. The YMCA can use the “profits” from its fitness centers to finance its charitable activities. To the extent it does that, it will avoid paying state and federal income tax on its profits.
But property taxes are something different from income taxes. The YMCA benefits from all the things the city (and other taxing jurisdictions) provide, ranging from public safety to schools to security for the mayor’s trip to Ghana. When it doesn’t pay its share, others have to pay. That means that others — you and me, for example — have less money available for the charitable (and other) activities they feel important. Even worse, I am forced to subsidize the charitable activities that the YMCA (or the Methodist Church, Boy Scouts, Girl Scouts, etc.) chooses to fund. This is especially true in Kansas, where low-income households pay a regressive sales tax on food.
When the YMCA — or any non-profit, for that matter — escapes taxation that other similar organizations must pay, it means that we all subsidize the charitable activities of these non-profits. It sustains a system in which special interest groups lobby to keep their advantages, and those who are not similarly blessed spend lavishly on campaign contributions and other lobbyists. Even when the organization is widely respected, as is the YMCA, this is wrong. It leads to cynicism as citizens realize that our laws are not applied uniformly, and that special interests feel they can buy their way to special treatment.
For their business-like activities, the YMCA, Larksfield Place, and Goodwill thrift stores should pay property taxes so they shoulder the same burden that the rest of us struggle under. That will spread the cost of government fairly, and let ordinary people themselves decide how to contribute their after-tax dollars.

Kansas tax revenue, January 2021
For January 2021, total Kansas tax revenue was 9.7 percent greater than January 2020. Over the seven months of the current fiscal year, tax revenue is 15.5 percent higher than at the same point of the previous fiscal year. (more…)

Wichita property tax rate: Up
The City of Wichita property tax mill levy rose slightly for 2020.
In 1994 the City of Wichita mill levy rate — the rate at which real and personal property is taxed — was 31.290. In 2020 it was 32.749, based on the Sedgwick County Clerk. That’s an increase of 1.459 mills, or 4.66 percent, since 1994. (These are for taxes levied by the City of Wichita only, and do not include any overlapping jurisdictions.)